Chemicals Manufacturing ERP Software
Explore BatchMaster Manufacturing
software for chemicals, paints, coatings, personal care, cosmetics
OUR ERP FOR CHEMICALS HELPS YOU BRING US INNOVATIVE PRODUCTS TO MAINTAIN OUR LIFESTYLES AND SURROUNDINGS
BatchMaster Software offers chemical manufacturing solutions that will help your company streamline operations and bring your products to market, faster and more cost efficiently, while complying with ever more stringent GHS regulatory mandates.
Whether you private-label, co-pack or produce your own line of chemical products, our chemical manufacturing software supports your unique requirements in the areas of product development, production, inventory, quality, costing, lot traceability, SDS compliance, planning, scheduling, and warehousing.
BatchMaster software applications are available on-premise and in the cloud.
GAIN VISIBILITY AND EFFICIENCIES WITH OUR CHEMICAL INDUSTRY ERP SOLUTIONS
If you don’t see your specific chemical segment below, please review our general chemical information and Contact Us to ask us about your specific chemical requirements.

Adhesives and Sealants

Flavors &
Additives
TOP CHALLENGES THAT CAN BE OVERCOME USING BATCHMASTER CHEMICAL MANUFACTURING SOFTWARE SOLUTIONS
Formula Additives:
Specifications can call for hundreds of liters for one additive, but only a few milliliters of another. Sometimes only small changes in the amounts of additives used in a batch job can have a significant impact on the finished product.
- Leverage automatic SKU unit of measure conversions with quantity levels defined down to 6 decimal places.
Formula Complexity:
Chemical formulations can have a complex multi-level hierarchy or have a set of active and filler additives. In some cases a finished good specification can be made up of 2 parts, each part with its own set of additives and properties, and when combined, the resulting finished product will have its own specifications.
- Define specifications manage the proportions of the components and properly summarize additive properties to ensure the accuracy of intermediates and finished goods quality and efficacy. Manage user chemical equations to calculate a product’s unique physical properties.
Ingredient Variability:
Managing concentrated additives, potencies and strengths, as well as any required dilutions can be challenging.
- Raw material variabilities by lot are managed in the formulation and batch production processes.
Safety Risks:
Natural ingredients can deteriorate over time, which can affect the quality and flavor of the seasoning, which can lead to expired inventory in the warehouse or worse yet, soon to be expired products on the retailer’s shelves, which will be returned.
- Allocate the right inventory in batch jobs by considering the expiration dates and rotation methods of lot controlled raw materials
Storage:
Some chemicals can be sensitive to temperature and humidity, and others may be of high value, which may require specialized storage areas to ensure product quality and security.
- Define the location rules for storing certain product types. Establish inspection plans to check the environments of certain facility areas. Establish stability tests for certain intermediates before they are used in batch jobs and for finished goods before they are shipping.
Regulatory compliance:
Chemical manufacturers must comply with a range of domestic and international regulations (e.g. GHS, REACH), related to product labeling, handling, transportation, and disposal, in addition to multi language and currency concerns.
- Document Management features and an integration of one of the leading SDS authoring solutions enable companies to generate the necessary documents and labels.
Quality control:
Faced with the variability in raw materials, the complexities in the production process, and possible regulatory penalties, chemical manufacturers must establish strict quality control standards.
- Define and execute customer specific QC tests, as well as record and manage deviations and reworks, to ensure that products meet customer and auditor requirements. Nonconformance and CAPA features support one’s continuous improvement initiatives.
Environmental impact:
The production of many chemicals can have a significant environmental impact, including air and water pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and waste generation.
- By-products can be defined in the formula to represent these areas, along with data collection and quality tests to track the resulting outputs.
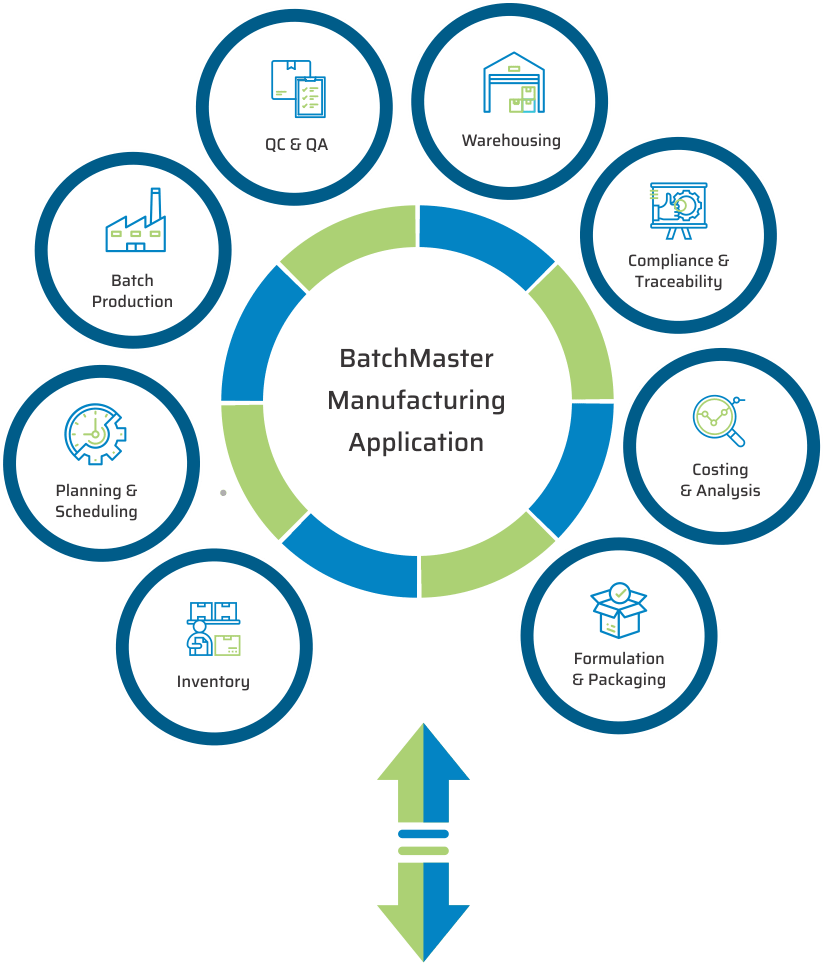
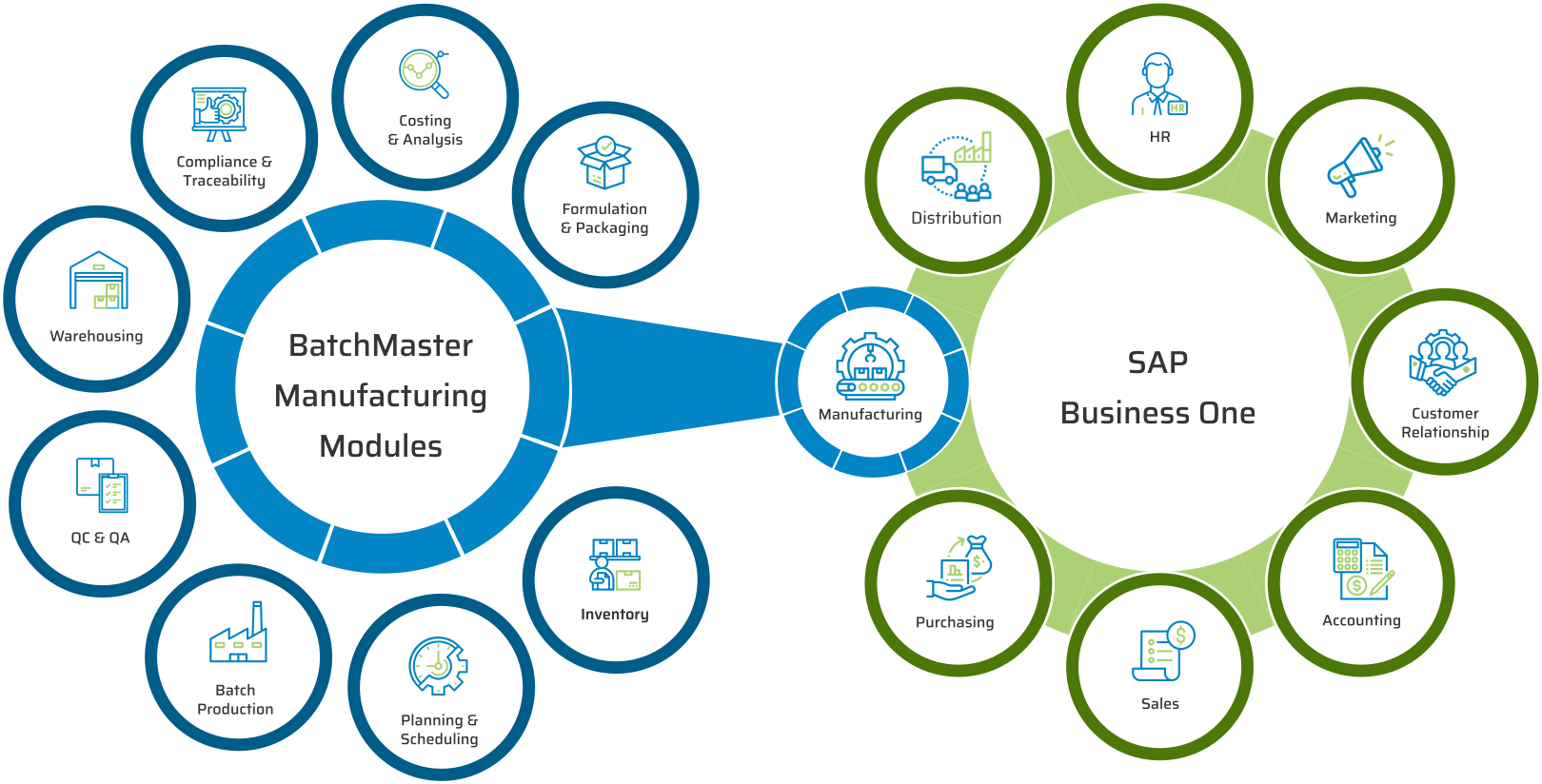
KEY MODULES FOUND IN OUR CHEMICAL MANUFACTURING SOFTWARE APPLICATION
BatchMaster chemical manufacturing software modules include formulation and packaging management, costing, inventory, production, quality, planning, scheduling, traceability & recall, SDS compliance, and mobile warehousing. All of these chemical manufacturing modules are available in our add-on chemical manufacturing application, which can be integrated to one’s existing financials, specifically QuickBooks, Sage 100 & 300, Microsoft Dynamics GP and SAP Business One. Our add-on chemical application is available on premise and in the cloud.


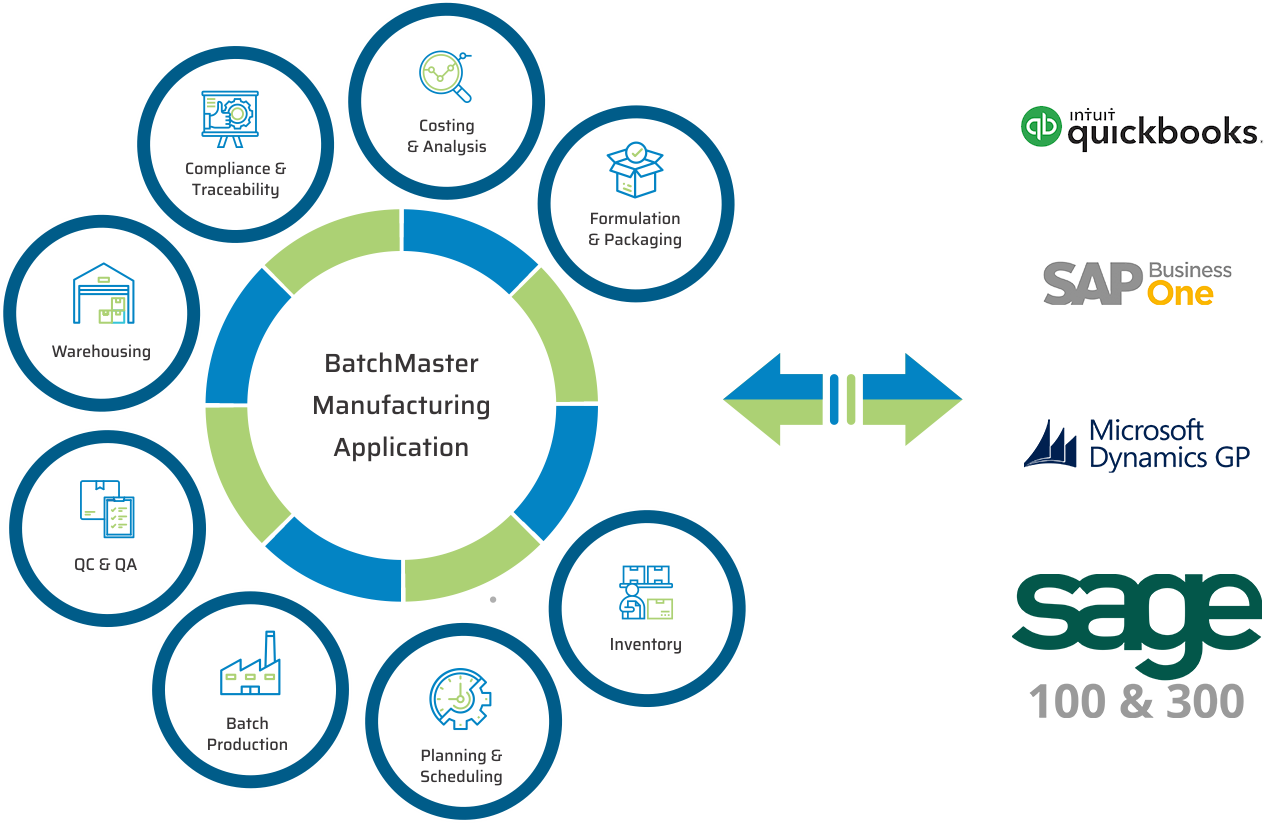

UPGRADE TO OUR ERP FOR CHEMICAL SOLUTION
BatchMaster ERP is the enterprise resource planning system designed to meet all of your critical business needs within a single, cohesive platform.
As an OEM partner of SAP. BatchMaster’s best-in-class business and industry capabilities for manufacturing have been natively embedded into SAP Business One, SAP’s market-leading and future-proof platform for small and midsize enterprises.
BatchMaster Software implements and supports our ERP application on our customers’ local server and in the cloud without the use of any third party consultants.
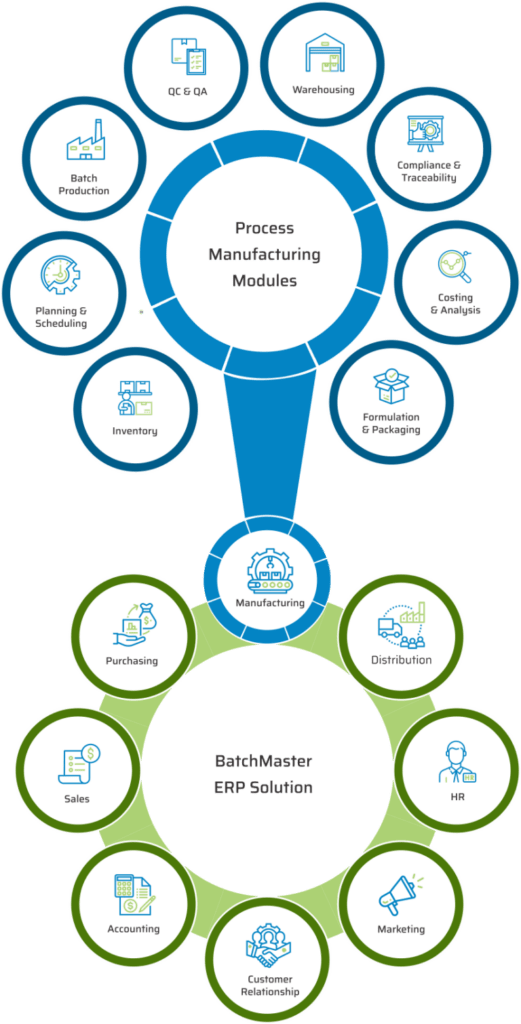
KEY MODULES FOUND IN OUR CHEMICAL ERP APPLICATION
BatchMaster Software chemical manufacturing modules are all available in our end-to-end ERP for Chemical solution, which also supports sales, purchasing, accounting, supply chain, and an inbuilt CRM. The application is available on premise and in the cloud.
KEY BENEFITS OF OUR CHEMICAL MANUFACTURING ERP SOFTWARE
1. Accelerate Product Development
- Track progress of samples
- Allow multiple developers to work on separate formula and packaging specs
- Employ industry and user defined equations
- Dynamically adjust formulas to meet physical and cost target values
- Perform side by side comparison of specs
- Initiate multi-level approval workflows
- Generate SDS reports and labels
2. Quickly Scale Up Production
- Dynamically adjust specs and yields based upon available inventory
- Reserve inventory for customer orders
- Auto link and schedule batch jobs
- Manage equipment and resource availability and capacities
- Auto generate lot numbers for intermediates and finished goods
- Execute production related tasks via mobile devices
- Automatically backflush inventory
3. Ensure Quality
- Establish QC and QA inspection, checklist, and special instruction libraries
- Mandate task acknowledgements and quality data collection
- Auto disposition any sub standard inventory
- Generate customized COA reports
- Manage deviation and non conformance situations
4. Control Costs
- Define fixed, tiered and variable labor costs within specifications
- Identify costs of consumables
- Run what if cost analysis
- Dynamically adjust recipes to meet cost target values
- Consolidate demand using MRP and MPS for discount bulk purchases
- Optimize resources utilization based upon MRP and MPS planning
- Analyze expected vs actuals
5. Ensure Compliance
- Dynamically adjust formulas to meet physical and cost target values
- Generate SDS reports and labels
- Generate bidirectional lot traceability reports
- Maintain full version control and audit history
- Auto assign lot numbers during receiving and production
- Track the variable characteristics of inventory
- View simultaneous dual units of measure
- Select the right inventory based upon expiry dates, certifications and status
- Reserve inventory for batch jobs
- Optimize inventory levels using automated planning and procurement
- Determine planning horizons and calendars
- Consider vendor delivery, order forecasts and planned production
- Prioritize customer orders
- Consolidate demand
- Link and schedule related batch order and runs
- Generate synchronized purchase orders
- Inbound receiving and putaway tasks
- Batch production functions and WIP inventory movements
- QC tests and special instruction tasks
- Outbound pick, pack and ship tasks
- Inventory adjustments, cycle counts and warehouse transfers
- Access real-time, accurate actionable data
- Employ drill down, role-based dashboards with graphical components
- Get quick data access using “favorite” shortcuts
- Customize industry inquiries and reports, as well as run ad-hoc queries
CONTACT US / REQUEST A DEMO
DOCUMENTS

Chemicals Brochure
A 6 page brochure addressing the challenges and requirements of chemical manufacturers, and the features and benefits of BatchMaster ERP for Chemicals.

Functional Checklist
VIDEOS

Speed Product Development

Streamline Production

Comprehensive QC & QA
Discover the quality control & quality assurance software features that can ensure the continuous flow of high quality products as you scale up production.

Lot Traceability & Recall
See how our lot management capabilities enable you to expedite traceability and recall activities
WHAT OUR CUSTOMERS SAY