Stage 6: Go-Live
This is the step where the ERP system becomes operational. At this point, all validated data is entered into the system, and daily operations begin on the new platform.
At this stage, some employees may still be confused despite training, so organizations should be prepared to manage this transition smoothly. Ensure the entire core team is present and prepared to answer questions, resolve issues, and support users through the change.
Stage 7: Maintenance
This stage focuses on ensuring the ERP system remains reliable, secure, efficient, and aligned with evolving business needs. Once the system is implemented is required. User feedback should be regularly reviewed and addressed to ensure the system operates smoothly and continues to meet evolving business needs.
What Are ERP Implementation Best Practices?
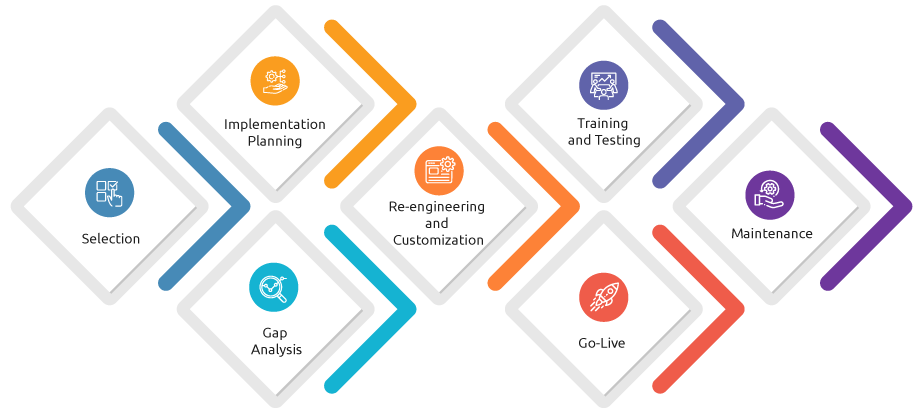
ERP systems have a lifecycle that begins with selection and planning, followed by implementation, customization, training, and testing. Once live, the system moves into the maintenance phase, where it’s continuously monitored, updated, and optimized.
Best practices include:
Understanding and managing each phase of the ERP lifecycle helps ensure smoother implementation, better adoption, and improved long-term value.
Conclusion
Understanding the lifecycle of an ERP system is essential for any organization planning to implement or upgrade its enterprise software. From careful selection and strategic planning to thorough training, testing, and ongoing maintenance, each stage plays a pivotal role in ensuring a successful ERP journey.
By following a structured, thoughtful approach, businesses can minimize disruptions, maximize return on investment (ROI), and ensure their ERP system evolves in line with their operational needs. Investing time and resources into every phase of ERP lifecycle management not only enhances system performance but also positions organizations for long-term growth and competitive advantage.
Contact us to schedule a demo and see our industry-specific features in action.